SAAS vs. iPaaS: Understanding the Key Distinctions in Cloud-Based Solutions
With cloud computing and digital transformation, businesses are constantly seeking the most efficient and effective solutions to streamline their operations and enhance productivity. Two prominent players in this arena are Software as a Service (SAAS) and Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS). While both offer cloud-based solutions, they serve different purposes and cater to distinct needs within an organization. This article will delve into the key differences between SAAS and iPaaS, exploring their features, benefits, and use cases to help you make informed decisions for your business.
Understanding SAAS (Software as a Service)
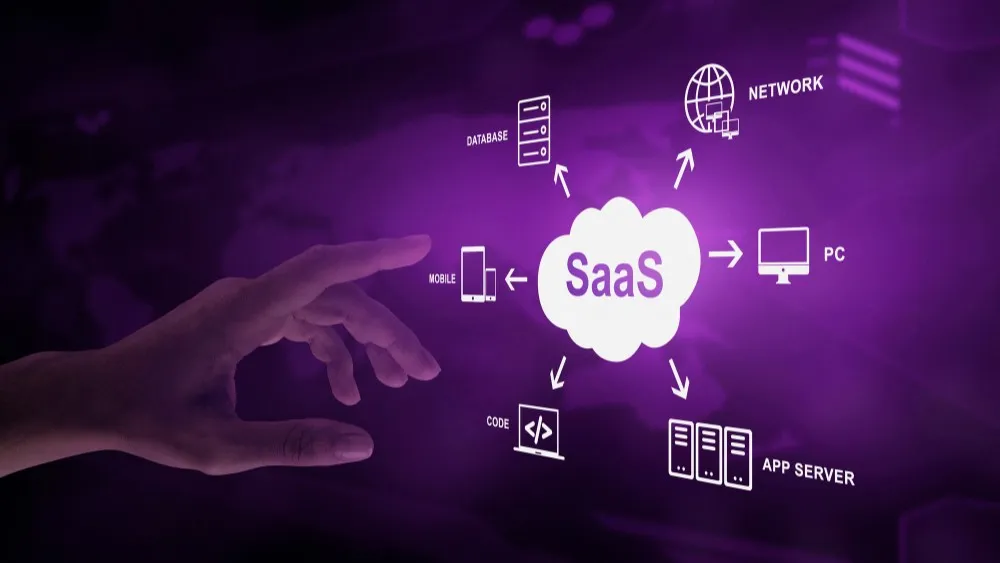
SAAS, or Software as a Service, is a cloud-based software delivery model where applications are hosted and maintained by a third-party provider and made available to users over the internet. Instead of installing and maintaining software on individual computers or servers, users can access the application through a web browser, typically on a subscription basis.
Key Features of SAAS:
- Web-based access: Users can access the software from any device with an internet connection.
- Centralized updates: The provider manages all updates and maintenance, ensuring users always have the latest version.
- Scalability: Businesses can easily adjust their usage and subscription levels based on their needs.
- Lower upfront costs: No need for significant hardware investments or on-premises infrastructure.
- Rapid deployment: SAAS solutions can be implemented quickly, often with minimal IT involvement.
Common SAAS Examples:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems like Salesforce
- Productivity suites like Google Workspace or Microsoft 365
- Project management tools like Asana or Trello
- Accounting software like QuickBooks Online
Understanding iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service)
iPaaS, or Integration Platform as a Service, is a cloud-based platform that enables organizations to connect and integrate various applications, data sources, and systems, both within the organization and across different cloud environments. It provides a centralized console for managing, developing, and maintaining integration flows.
Key Features of iPaaS:
- Pre-built connectors: iPaaS platforms often offer a wide range of pre-built connectors for popular applications and systems.
- Data mapping and transformation: Tools for mapping data fields between different systems and transforming data formats.
- API management: Capabilities for creating, publishing, and managing APIs.
- Workflow automation: The ability to create and manage complex workflows across multiple systems.
- Monitoring and analytics: Real-time monitoring of integration processes and performance analytics.
Common iPaaS Use Cases:
- Syncing customer data between CRM and marketing automation systems
- Integrating e-commerce platforms with inventory management systems
- Connecting on-premises legacy systems with cloud-based applications
- Automating business processes across multiple departments and systems
Key Differences Between SAAS and iPaaS
- Primary Purpose SAAS: Provides ready-to-use software applications for specific business functions. iPaaS: Offers a platform for integrating and connecting various applications and systems.
- User Focus SAAS: Typically used by end-users within a specific department or function. iPaaS: Primarily used by IT teams, developers, and integration specialists.
- Customization and Flexibility SAAS: Often offers limited customization options within the confines of the application. iPaaS: Provides high levels of flexibility and customization for creating unique integration solutions.
- Scope of Functionality SAAS: Focused on delivering specific functionality within its domain (e.g., CRM, accounting). iPaaS: Designed to work across multiple systems and applications, facilitating data flow and process automation.
- Implementation Complexity SAAS: Generally easier to implement, often requiring minimal technical expertise. iPaaS: May require more technical knowledge and planning for effective implementation and management.
- Data Handling SAAS: Stores and manages data within its own ecosystem. iPaaS: Facilitates the movement and transformation of data between different systems without necessarily storing it.
- Scalability SAAS: Scales in terms of user licenses and features within the application. iPaaS: Scales in terms of the number and complexity of integrations and data volume handled.
- Cost Structure SAAS: Typically based on per-user or per-feature pricing models. iPaaS: Often priced based on the number of connections, data volume, or API calls.
Choosing Between SAAS and iPaaS
The choice between SAAS and iPaaS depends on your organization’s specific needs and challenges:
Choose SAAS when:
- You need a specific software solution for a particular business function.
- Your goal is to lower IT infrastructure and maintenance expenses.
- Rapid deployment and ease of use are priorities.
- You prefer a standardized solution with regular updates.
Choose iPaaS when:
- You need to integrate multiple applications and systems.
- You want to automate complex business processes across different platforms.
- You require flexibility in creating custom integration solutions.
- You need to connect cloud-based services with on-premises systems.
The Impact on SEO and Backlinks
While SAAS and iPaaS are primarily focused on business operations, they can indirectly impact a company’s SEO efforts and backlink strategy:
SAAS and SEO: Many SAAS providers offer white-label or customizable solutions that allow businesses to maintain their branding and domain authority. This can be beneficial for SEO as it enables companies to keep traffic and engagement metrics associated with their own domain. Additionally, some SAAS solutions, especially in the marketing and content management space, often include SEO tools or features that can help improve a website’s search engine visibility.
iPaaS and Backlinks: iPaaS solutions can play a crucial role in managing and leveraging backlinks across different platforms. By integrating various systems, such as CMS platforms, social media management tools, and analytics software, businesses can more effectively track, analyze, and optimize their backlink profiles. This integrated approach allows for better identification of high-quality link opportunities and more efficient outreach processes.
Moreover, the use of iPaaS for seamless data integration can lead to improved user experiences on websites, potentially increasing the likelihood of earning natural backlinks. For instance, by integrating product inventory systems with e-commerce platforms, businesses can ensure up-to-date information across all channels, reducing user frustration and potentially encouraging more referrals and linkbacks.
The Future of SAAS and iPaaS
As digital transformation continues to accelerate, both SAAS and iPaaS are likely to evolve and grow in importance:
SAAS Evolution:
- Increased AI and machine learning integration for more intelligent and predictive capabilities.
- Greater emphasis on vertical-specific solutions tailored to particular industries.
- Enhanced mobile-first approaches to cater to the growing remote workforce.
iPaaS Evolution:
- Adoption of low-code/no-code interfaces to make integration more accessible to non-technical users.
- Expansion of AI-driven automation for more complex integration scenarios.
- Increased focus on real-time data processing and event-driven architectures.
Conclusion
While SAAS and iPaaS are distinct solutions serving different primary purposes, they are both integral to the modern cloud-based business ecosystem. SAAS provides ready-to-use applications that can quickly solve specific business needs, while iPaaS offers the flexibility and power to connect and integrate various systems, enabling more comprehensive and tailored solutions.
Understanding the differences between these two approaches is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their technology stack and digital operations. By leveraging both SAAS and iPaaS where appropriate, organizations can create a more efficient, integrated, and scalable IT environment that supports their growth and innovation goals.
As you evaluate your business needs, consider how SAAS solutions can address specific functional requirements and how iPaaS can tie these solutions together into a cohesive, automated ecosystem. This strategic approach to cloud-based services can not only improve operational efficiency but also contribute to better data management, customer experiences, and, ultimately, business success in the digital age.